Climate-related Risk Strategies
Climate Policy
Commitment | FENC aligns with the Paris Agreement by setting its carbon reduction targets and responding to climate change with the overarching goal of limiting the temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Through phased decarbonizing actions targeting its own operations and forming coalitions with supply chain partners, FENC is promoting green transformation and building climate resilience within the industry. |
Target | As the world moves towards carbon reduction in the net zero era, FENC stays in line with this trend and boosts its competitiveness by recalibrating its carbon reduction targets upward in 2024. With 2020 as the base year, the Company is aiming for 30% reduction in scopes 1 and 2 GHG emissions by 2025 as the near-term target, 50% by 2030 as the mid-term target, and net zero emissions by 2050 as the long-term target. At FENC’s Polyester Business, the target has been set for 42% reduction in scope 3 emissions by 2030 with 2022 as the base year. To support the net zero vision and steer carbon reduction actions within the industry chain, FENC has also established new targets for the low-carbon transition in 2024, setting the trajectory for 50% carbon reduction, 50% green raw materials and 50% green products by 2030. By transforming the entire operation through the low-carbon model, including the raw materials, production processes and products, FENC is leading the industry into a green future. |
Strategy | 1. Improve energy efficiency. 2. Adopt low-emission fuel alternatives. 3. Develop renewable energy. 4. Utilize CCU. 5. Foster raw material transition. |
Note: The scope of the commitment includes our own operations as well as key value chain partners, including raw material suppliers and other business partners.
Building Climate Resilience
The effects of climate change and global warming are growing severe. To mitigate and adapt to climate risks, FENC adopted the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) assessment in 2019. Each year, the Company discloses the results in its annual Sustainability Report and on the Company website. In 2023, the Company issued its first TCFD Report. Leveraging the TCFD framework and sustainability disclosure standards from IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures, the report is an assessment of climate-related financial risks and opportunities on FENC Businesses and production sites with which the Company wishes to cultivate a resilience mindset.
⇥ FENC Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) Report
Climate Governance
FENC's climate governance is led by the Board, which oversees the Company's climate-related strategies and management guidelines, and the Sustainability Committee, a functional committee, has also been set up at the Board level. In addition, the Sustainability Implementation Committee was established under the Company's organizational structure with the President of Corporate Management as the convener. The committee consists of representatives from each Business, including the production sites, business units and the administrative departments, working collectively to promote the Company's climate-related risk mitigation, adaption and low-carbon transition. Among these tasks, matters related to GHG and energy management are under the responsibility of the Energy Task Force, and the Sustainability Team under the Corporate Staff Office compiles sustainability performance data and reports to the Board and the Sustainability Committee. The Presidents and Chief Operating Officers of each Business and the Energy Task Force present climate-related issues during the Board and internal meetings at least annually.
The Organizational Chart of Climate-Related Risk and Opportunity Management
.png)
Climate-Related Risk and Opportunity Management System
In order to fully grasp the impact of climate-related risks and opportunities on the company, FENC has established a climate-related risk and opportunity management system. The Sustainability Implementation Committee is responsible for promoting the management of climate-related risks and opportunities and formulating a bottom-up risk and opportunity reporting system to implement a top-down tracking and supervision mechanism by the Board of Directors.
Climate-Related Risk and Opportunity Management Procedure
.png)
Identifying Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities
Based on the TCFD framework, FENC established a comprehensive workflow to identify climate-related risks and opportunities. First, climate-related issues are collected. The climate risks and opportunities are then identified and screened using the Representative Concentration Pathway 8.5 (RCP8.5) and Net Zero Scenario (NZE) analysis to arrive at 18 that are most relevant to FENC. The risks and opportunities are assessed for impacts based on the time horizon, likelihood of occurrence and degree of impact for the prioritization of major climate risks and opportunities.
Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities Identification Process
.png)
Scenario for Risks and Opportunities
| Scenario | SSP5-8.5 | NZE |
| Type | Physical risks | Transition risks and opportunities |
| Detail | The SSP5-8.5 scenario is presented in the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) under the assumption of absence in climate actions from all countries, which would result in the highest CO2 concentration. It could be regarded as the most stringent climate scenario. Adopting this scenario would help FENC assess the degree of impacts under the most extreme climate challenges. | The NZE scenario is published by IEA. To limit the global temperature rise to 1.5 °C, the NZE scenario represents a path to net zero emissions by 2050 for the world and is considered the most extreme reduction scenario. As the surge of carbon reduction policies sweeps through the world, adopting the NZE scenario would help FENC gain competitive advantages by taking preemptive strikes. |
| Parameter | Assuming the worst case scenario (SSP5-8.5), it is projected that by 2050, the annual average of total precipitation in East Asia, including Taiwan and mainland China, will see a 15% surge, and the heaviest single-day precipitation will increase by 20% in intensity, accompanied by the occurrence of extreme weather events such as typhoons, floods and rainstorms. | Assuming the NZE scenario, carbon fees/taxes are levied across all sectors in all regions: By 2050, the carbon price will move up to US$250/tCO2e in advanced economies and US$200/tCO2e in non-advanced economies. |
| Projected Temperature Rise by the End of This Century | >4℃ | ~ 1.5℃ (Consistent with the commitment under the Paris Agreement) |
List of Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities
No. | Type | Risk and Opportunity Issues | Potential Financial Impact | Time Horizons |
| 1 | Transition Risk | Regulations on greenhouse gas reduction and renewable energy | To meet regulatory requirements, FENC has expanded the deployment of its renewable energy installations, resulting in an increase in operating costs. | Medium term |
| 2 | Transition Risk | Carbon pricing mechanism | The regions where the company's production sites are located have implemented carbon pricing policies and imposed carbon fees/taxes on carbon emissions. It is estimated that the rising operating costs from carbon fees or taxes may peak in 2050. | Long term |
| 3 | Transition Risk | Carbon border tax | To avoid carbon leakage, countries have formulated carbon border taxes for imported products. FENC's operating costs will rise due to the import duty imposed on its exports. | Medium term |
| 4 | Transition Risk | Transition to low-carbon technologies and fuels | In order to achieve low-carbon transition, FENC has replaced existing conventional equipment and machines of high energy consumption and high carbon emissions with high-efficiency and low-carbon ones, resulting in an increase in both capital expenditure and production cost. | Medium term |
| 5 | Transition Risk | Research and development in net zero technologies | In the face of market demand, FENC has continued to develop net-zero technologies and green and low-carbon products, resulting in an increase in its R&D cost. | Medium term |
| 6 | Transition Risk | Changes in customer behavior | Considering the impact of climate change, customers prefer to use lower-carbon products and demand FENC should reduce carbon emissions. Failure to meet customer requirements may result in customer attrition and revenue loss. | Medium term |
| 7 | Transition Risk | Loss of investment attractiveness | Due to the inability to maintain good ESG performance, the willingness of investors to invest (or finance) will be reduced, resulting in a decline in FENC’s market value or an increase in funding costs. | Medium term |
| 8 | Transition Risk | Industry stigmatization | With the rising awareness of environmental protection, any negative publicity related to carbon emissions may cause government and people living in the surrounding area to demand FENC cut down or even stop production, resulting in reduced production capacity and revenue. | Long term |
| 9 | Physical Risk | Increased severity and frequency of extreme weather events such as cyclones and floods | Damage to equipment caused by extreme weather events may reduce production capacity or increase maintenance costs. | Long term |
| 10 | Physical Risk | Rising sea levels | Under the impact of climate change, if the company's production site is located in a high-risk area prone to sea level rise, it may cause the assets and equipment to be submerged, leading to asset damage. | Long term |
| 11 | Physical Risk | Increased severity and frequency of extreme weather events such as cyclones and floods (supply chain) | The locations of suppliers or the shipping routes are affected by climate change, causing raw materials to not arrive at the factory on schedule, resulting in a reduction in output. | Medium term |
| 12 | Physical Risk | Rising mean temperatures | Outdoor operations need to be suspended due to high temperatures, leading to prolonged working time and an increase in labor costs. | Long term |
| 13 | Physical Risk | Changes in precipitation patterns and extreme variability in weather patterns | Extreme precipitation patterns, such as an increase in consecutive dry days, heighten the risk of water shortages. In order to enhance the resilience of water resources, FENC has invested in water-saving facilities and initiated water conservation measures, resulting in an increase in capital expenditure and operating costs. | Short term |
| 14 | Opportunity | Reduced water usage and consumption | When water shortages occur, FENC's water resources management measures with better resiliency, compared to its peers, help to avoid a decline in production output or delayed shipments, thereby increasing sales revenue. | Medium term |
| 15 | Opportunity | Use of lower-emission sources of energy | By using renewable energy or other low-carbon energy sources to meet customer requirements, FENC can increase product price bargaining power or order volume, thereby increasing sales revenue. | Medium term |
| 16 | Opportunity | Development or expansion of low emission goods and services | The company continues to reduce product carbon emissions, meeting customers' emission reduction requirements, increasing product price bargaining power or order volume, thereby increasing sales revenue. | Short term |
| 17 | Opportunity | Development of new products or services through R&D and innovation | Through the research and development of green products, FENC can meet customer requirements, thereby increasing sales revenue. | Short term |
| 18 | Opportunity | Access to new markets | As recycling policies are promoted and implemented in various countries, the overall environment is conducive to FENC's expansion of its market for recycled products, thereby increasing sales revenue. | Short term |
Note:
1.Short term refers to the period between 2024 and 2025; medium term 2026 and 2030; long term 2031 and 2050.
2.Climate-related risks and opportunities were initially assessed with reference to the TCFD framework and international industry trends, resulting in a comprehensive long list of climate risks and opportunities. Although legal risk (Litigation risk) was included in the initial list, the assessment of material risks and opportunities most relevant to the Company concluded with the selection of the 18 key issues listed above.
Identification Outcome of Material Climate Risks and Opportunities
Carbon pricing mechanism, carbon border tax and changes in customer behavior are identified in the assessment as the top three material risks; access to new markets, use of low-emission sources of energy, and development or expansion of low-emission goods and services are the top three material opportunities. FENC conducted quantitative financial analysis targeting the six issues and formulated management strategies with implementation measures to galvanize FENC’s climate resilience.
Though physical risks were not among the material climate risks determined during the identification process, FENC decided to proceed with the routine risk ranking projects to reduce operational risks at its production sites.
Climate-Related Risk Matrix
.png)
Climate-Related Opportunity Matrix
.png)
Financial Impact Analysis on Material Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities
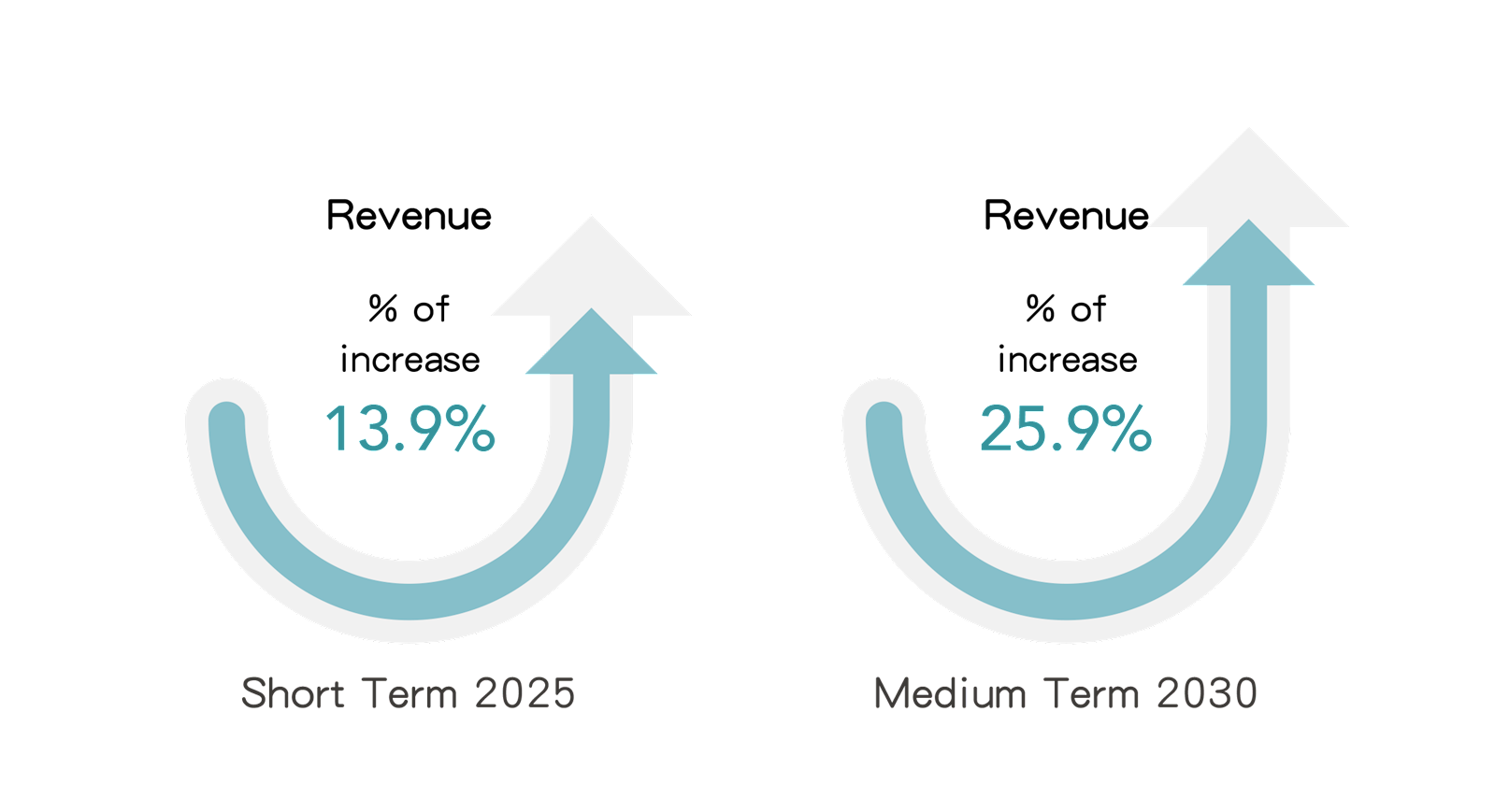
Specific to the top three risks and opportunities based on the outcome from the level of impact identified, FENC conducted a financial impact analysis on the potential climate-related risks and business opportunities to estimate the likely valuation of the financial impact in 2025 to 2030.
Note: The potential financial impact on revenue of these six issues are related to the overall revenue of FENC's production business. The impacts are presented as a percentage of the revenue of the reporting year.
1. Risk Issue: Carbon Pricing Mechanism
(1) Explanations on the Impact
Under the increasingly severe impacts of climate change, mainland China officially launched its nationwide carbon emissions trading system on July 16, 2021. Based on historical emissions and future development for each industry, emission benchmarks are calculated, and enterprises are allocated free carbon emission allowances. Companies are then allowed to trade these allowances in the carbon market. The system started with the power sector, with consideration to include eight key industries such as chemicals and steel. In Taiwan, the Climate Change Response Act was promulgated on February 15, 2023. As part of Taiwan’s roadmap toward net-zero emissions by 2050, the imposition of carbon fees was introduced. The three sub-laws of the carbon fee system were announced in August 2024, officially ushering Taiwan into the era of carbon pricing. In summary, FENC’s production sites will face the need to either pay carbon fees or purchase carbon allowances in the future, thereby leading to increased operating costs.
(2) Scenario Description
This issue uses the estimated carbon prices for various countries at different times under the NZE scenario set out in the IEA’s 2024 WEO to assess the financial impact on the revenue of the company's production business before 2030.
(3) Potential Financial Impact

2. Risk Issue: Carbon Border Tax
(1) Explanations on the Impact
In response to the risk of carbon leakage, the measure of carbon border tax will become an international trend. A case in point is the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which imposes charges on imported goods from countries and regions with relatively loose carbon emission restrictions. In the future, if countries, like the U.S., Japan, and South Korea, also begin to plan carbon border tax or to explore countermeasures against carbon leakage, the costs for FENC’s exported products are likely to be increased.
(2) Scenario Description
This issue assesses the financial impact on the company's revenue from export products in its production business under the NZE scenario set out by the IEA’s 2024 WEO report. The product may be affected by carbon border tax by 2030.
(3) Potential Financial Impact
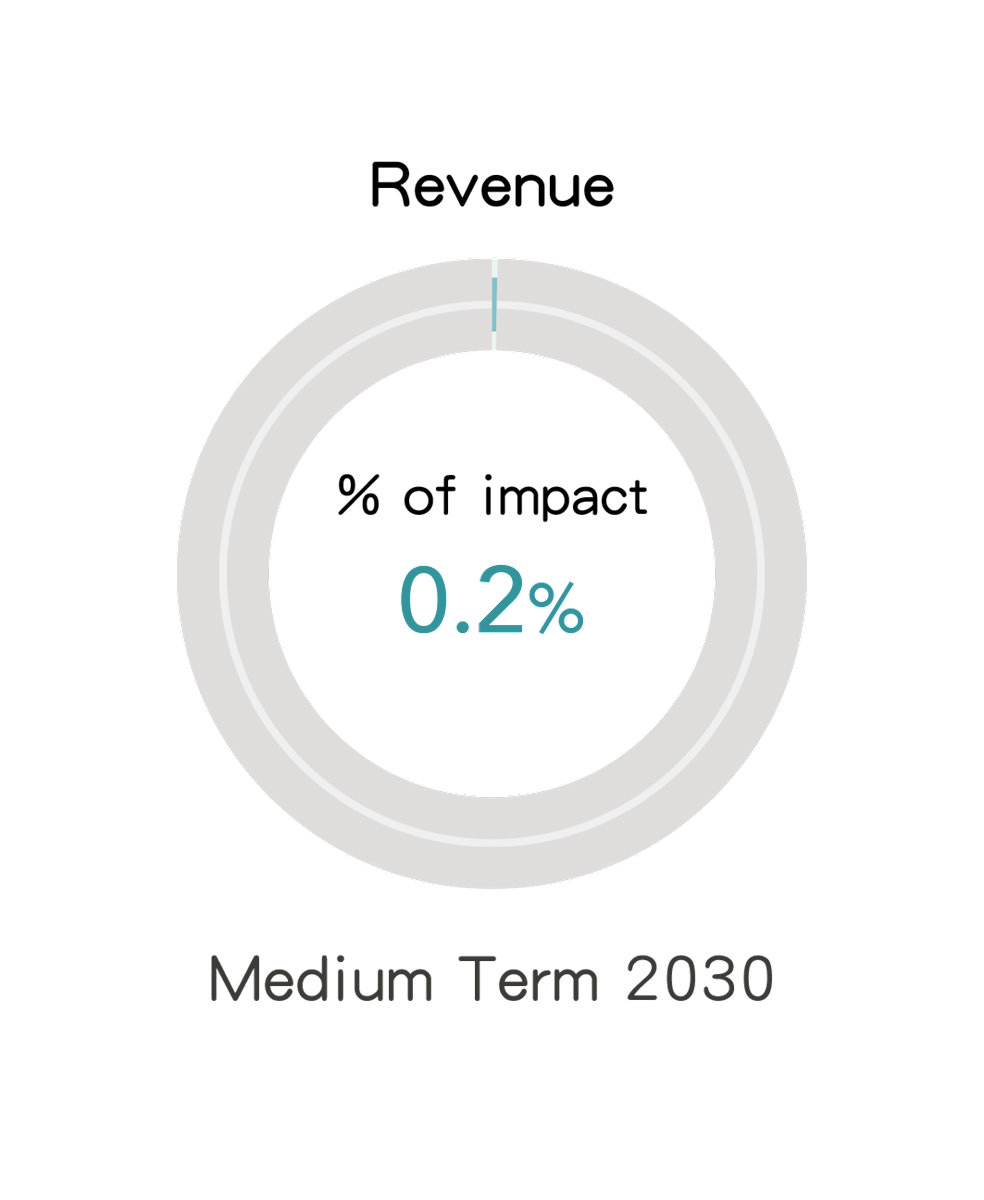
Note: The countries or regions to which FENC exports have not planned to implement border carbon tariffs in 2025.
3. Risk Issue: Changes in Customer Behavior
(1) Explanations on the Impact
Net Zero policy has been adopted and implemented across the world. To achieve net zero in value chain, international brands require value chain partners to reduce product GHG emissions year by year, and to develop specific carbon reduction plans to ultimately achieve net zero emissions. FENC is faced with rising sustainability awareness among many downstream customers, and their tendency to source products from companies that actively reduce GHG emissions. If the company cannot continue to cut down GHG emissions in the future, it may lose some customers and market share, thereby affecting its sales revenue.
(2) Scenario Description
This issue uses the NZE scenario set out by the IEA in the 2024 WEO report. Under this scenario, all industry players have activated net zero emission strategies, requiring value chain partners to reduce carbon emissions. An assessment was conducted to evaluate the potential financial impact on the revenue of the company's production business before 2030.
(3) Potential Financial Impact
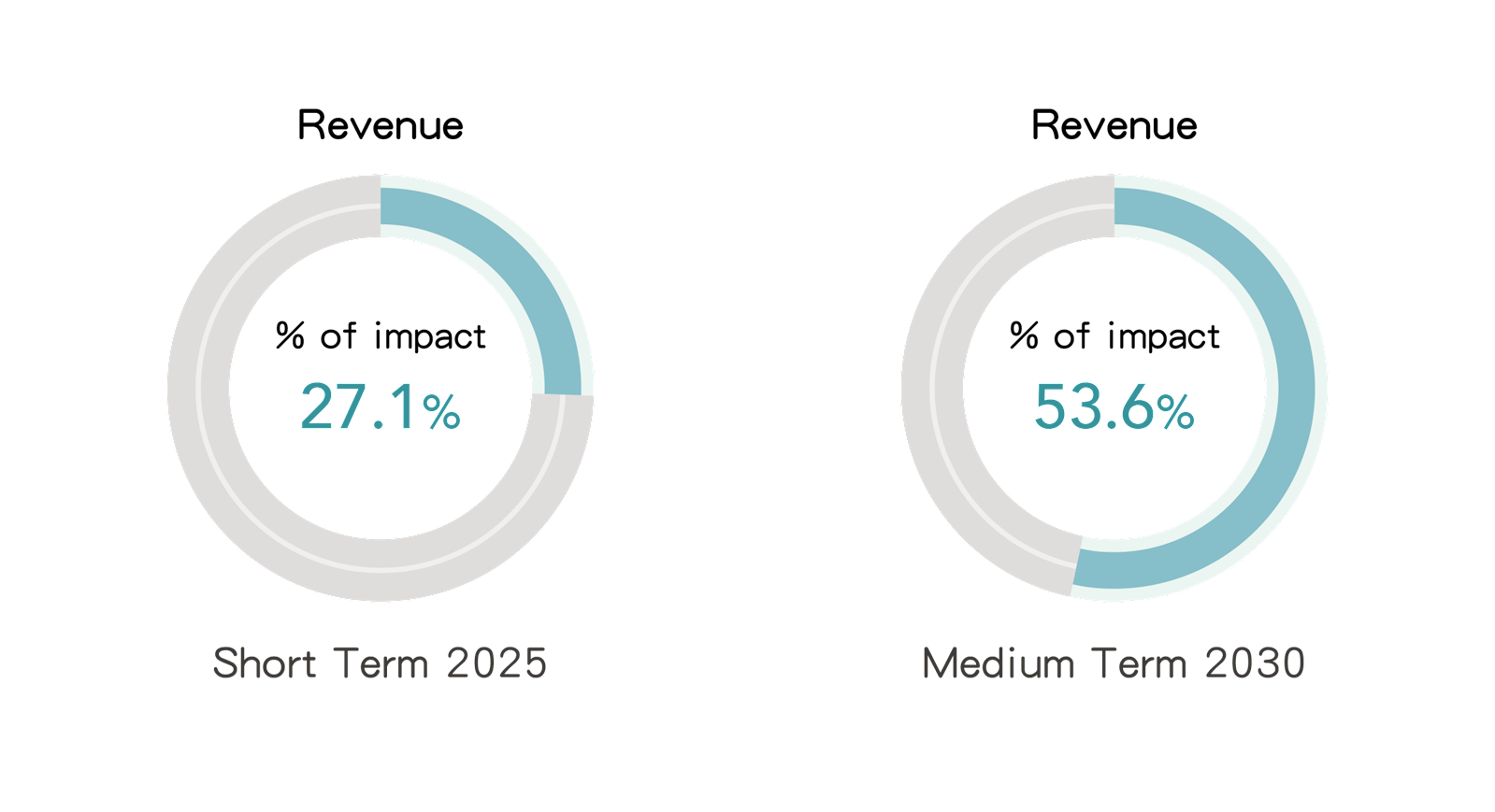
4. Opportunity Issue: Use of Lower-Emission Sources of Energy
(1) Explanations on the Impact
Impacted by the international trend of net-zero emissions, the momentum of a company’s green energy policies will gradually move from the company itself to its value chain, requiring value chain suppliers to implement emission reduction measures. By building renewable power generation facilities or purchasing renewable energy certificates, the GHG emitted by the company’s electricity consumption can be reduced. According to FENC’s 2024 GHG inventory, Scope 2 emissions (indirect GHG emissions from imported electricity, heat or steam) account for about 42% of Scope 1 and 2 emissions from 21 production bases in the production business. FENC continues to build renewable power generation facilities in the future, it can not only meet the requirements of value chain customers and ensure order volume, but also enhance product value by meeting customers' renewable electricity requirements, and thereby increase sales revenue.
(2) Scenario Description
This issue uses the NZE scenario set out by the IEA in the 2024 WEO report. In this scenario, customers will demand the company expand the use of renewable electricity. FENC assessing the potential financial impact on the revenue of the company's production business by 2030.
(3) Potential Financial Impact
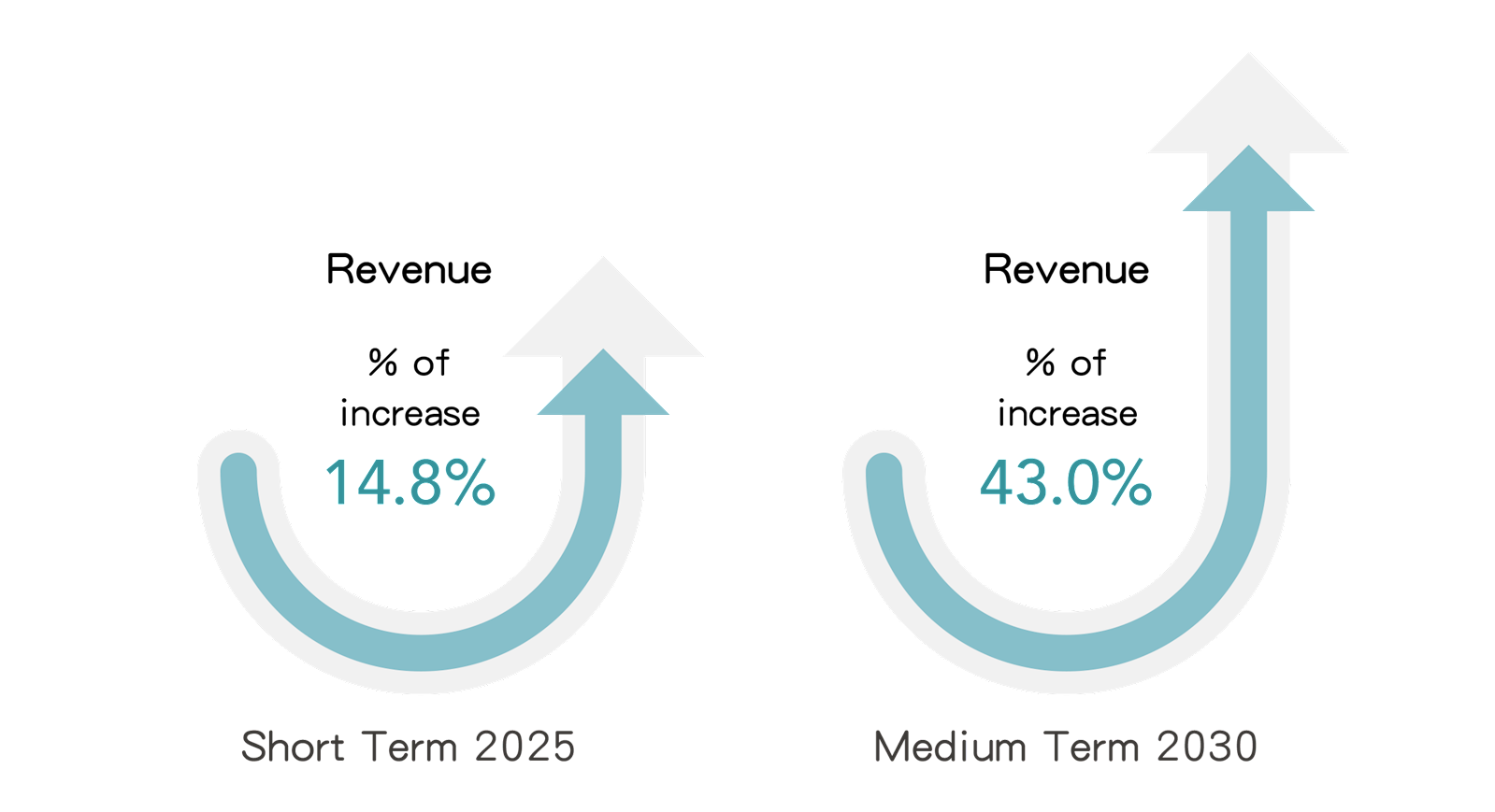
5. Opportunity Issue: Development or Expansion of Low Emission Goods and Services
(1) Explanations on the Impact
The Paris Agreement set the goal of containing global temperature rise within 1.5°C. In order to continuously reduce the intensity of carbon emissions, companies have extended their emission reduction policies from themselves to supply chain companies, requiring the latter to provide products with lower unit GHG emissions. Going forward, if FENC continues to reduce GHG emissions per unit of production, it will be able to secure orders and enhance product value, which in turn will lead to an increase in sales revenue.
(2) Scenario Description
This issue adopts the NZE scenario set out by the IEA in the 2024 WEO report, assessing the potential financial impact on the revenue of the company's production business before 2030. Under this scenario, customers will continue to increase demand for FENC's green products in order to achieve their net zero goals.
(3) Potential Financial Impact
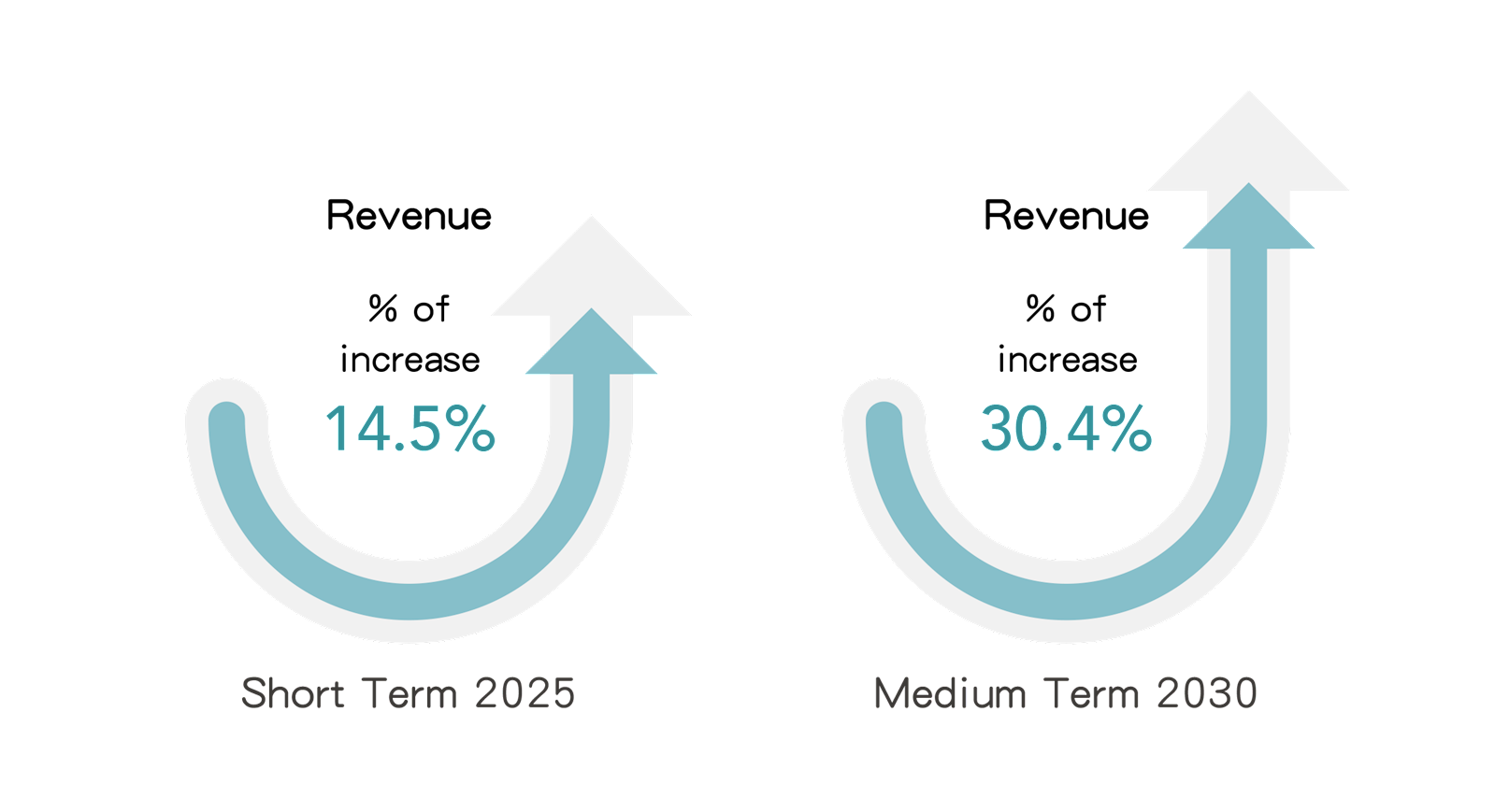
6. Opportunity: Access to New Markets
(1) Explanations on the Impact
To reduce GHG emissions from single-use chemical industry products and achieve the goal of net-zero emissions, many governments have introduced requirements for packaging materials to contain a certain proportion of recycled content, or have advanced various recycling policies. Spain, starting in January 2023, began levying a tax on virgin plastics. The United Kingdom, from April 2025, will impose a plastic packaging tax on products with less than 30% recycled content. Italy is scheduled to implement a similar measure in July 2026. In addition, in December 2024, the European Union officially adopted the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), setting a target for single-use PET bottles to contain 30% recycled content by 2030. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency announced the National Recycling Strategy in 2021, aiming to raise the national recycling rate to 50% by 2030. FENC possesses mature recycling manufacturing capabilities and continues to develop new technologies. In 2024, FENC ranked first in the world in the production scale of food-grade recycled polyester (rPET). Looking ahead, as global recycling rates continue to rise, the expansion of FENC’s production bases will further drive growth in sales revenue from recycled products.
(2) Scenario Description
This issue uses the NZE scenario set out by the IEA in the 2024 WEO report to assess the likely financial impact on the revenue of the company's production business before 2030 as customers’ demand for the company's recycled products will increase in this scenario.
(3) Potential Financial Impact
Material Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities: Strategies and Response Plans
Material Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities Issues | Strategies and Response Plans | 2024 Management Costs |
Carbon pricing mechanism | GHG emissions at each production site are monitored, and FENC aims to achieve its short-, mid- and long-term GHG reduction targets through the five major low-carbon transition strategies to ultimately accomplish net zero by 2050. Meanwhile, the Company adopted the internal carbon pricing mechanism as a management tool that incentivizes carbon efficiency during the evaluation of energy and emission reduction projects. Carbon costs are also included in the monthly management reports of each Business as a decision-making reference. | NT$ 2,296 million invested in carbon reduction projects |
Carbon border tax | The financial impact is positively correlated with the carbon emissions per unit of production. To mitigate the risk, FENC will implement strategies, such as expanding the use of alternative low-carbon materials, improving energy efficiency, adopting low-emission fuel alternatives, and deploying more renewable energy facilities to reduce the carbon footprint of its production processes. | |
Changes in customer behaviors | In response to customers' demand for low-carbon products in the value chain, we will aggressively reduce GHG emissions per unit of production, and GHG emissions in the production processes by improving energy efficiency, adopting low-carbon fuels, and using renewable energy. | |
Use of lower-emission sources of energy | Renewable electricity will be acquired through means such as long-term electricity purchase agreements. FENC will also continue expanding the installed capacity of renewable energy, such as solar and biogas power, at its worldwide production sites for self-use. The company expects the use of renewable electricity across its global sites to reach 250 GWh by 2025, in order to meet customer expectations. | NT$ 1,218 million for renewable energy deployment and procurement |
Development or expansion of low emission goods and services | FENC continuously promotes the research and development of technologies related to green products, including products which can replace petroleum-based raw materials (Replace), and can be recycled (Recycle), as well as reduce energy and resource consumption (Reduce). FENC has been expanding its green product production capacity to meet the needs of customers in the value chain. | NT$576 million for R&D of green products |
Access to new markets | FENC keeps on researching and developing circular recycling technology and the applications of multiple recycling products, while paying attention to the trend of recycling-related laws and regulations in various countries. It has deployed all-encompassing circular technology on land, ocean and air, and expanded its production capacity of recycling and circular products with optimal capacity planning, aiming to become the World No. 1 in rPET production capacity. | NT$2,018 million for production capacity expansion of rPET products |
Note: The investment of NT$2,296 million in carbon reduction projects includes NT$1,218 million for the construction and purchase of renewable energy.
Climate Risk Metrics and Targets
Target and Progress of GHG Reduction
.png)
Note:
1. The disclosure of GHG emissions includes Scope 1 and Scope 2, covering 100% of the main production sites of the production business, with 2020 as the base year.
2. Carbon credits are excluded from contribution towards the GHG reduction targets of FENC.
Low-Carbon Transition Strategies
- Improve Energy Efficiency: FENC improves energy efficiency by optimizing the production process, facilities and energy management. Energy projects in the pipeline include a new cogeneration system, capitalizing on thermal and electrical power by recycling and reusing waste heat.
- Adopt Low-Emission Fuel Alternatives: FENC’s short-term carbon reduction plans call for replacing high-emission fuels such as coal or heavy oil with low-emission alternatives such as natural gas and biofuels. The mid- to long-term plans are to be fully transitioned, replacing natural gas completely with hydrogen fuels.
- Develop Renewable Energy: FENC is investing heavily in renewable energy equipment and increasing the percentage of renewable energy yearly in its energy mix.
- Renewable energy generators: 21.9MW installed in 2024 with 25 GWh and 38.2MW in 2025 with 47 GWh expected in capacity
- Long-term electricity purchase agreement: At least 100 GWh purchased per year starting from 2023
- Utilize CCU: The technology is utilized to convert carbon dioxide into usable products. FENC plans to focus on capturing and reusing the carbon dioxide from the boiler exhaust in the future and continue its research on microalgae-based, bio-integrated carbon capture technologies.
- Foster Raw Material Transition: FENC adopts low-carbon alternatives with focuses on recycling and biomass. The Company has been applying its core strengths towards the development of environmentally friendly and low-emission materials and expanding the applications of these innovations.








