Occupational Safety and Health
We strive for reducing workplace risks to protect the health and safety of staff and contractors. Our goals are to achieve zero occupational injury and incident.
Implementation of Occupational Safety and Health Management
Occupational Health and Safety Policy and Target
To establish a safe and healthy workplace with comfort while consistently lowering the rate of workplace accidents and disasters, FENC established Occupational Health and Safety Policy as the highest guiding principle governing the management of safety and health of the Company. With “risk control” and “continuous improvement” as the management principle, operational safety is our utmost concern. The Company takes an active stand toward improving the work environment, manufacturing equipment and operational approaches. Based on risk assessments and other mechanisms, the Company sets up prioritization and action plans to ensure the safety and health of the workers (including employees and who are not employees (the contractors of the Company)) and stakeholders.
⇥ Occupational Health and Safety Policy
Executive Support and Involvement in Occupational Safety and Health
During the quarterly FENC Board meetings, the president from each Business presents the Occupational Safety and Health Management Report compiled by the Labor Safety and Health Department from the headquarters. In 2024, 4 reports were presented. The Board serves the supervisory role and conducts review and questioning over the report. Improvements needed will be acted upon at production units based on Board resolutions to ensure proper occupational safety and health management.
Continuous Operation of Occupational Safety and Health Management
As of the end of 2024, the occupational safety and health management system has been implemented at all FENC sites.
- A total of 19 sites, representing 100% of the scope of this report, have implemented the system, covering 100% of the workers (employees and contractors). Internal audits cover 100% of FENC production sites. Among them, 17 have obtained ISO 45001 certification and undergone external audits, which cover 90% of FENC workers, including employees and contractors.
- Conducts related to occupational safety and health management; worker engagement; consultation and communication; prevention and mitigation of occupational safety and health impacts directly related to job duties are carried out in accordance with the stipulations in the occupational safety and health management system.
Risk Identification, Assessment and Control
Occupational Safety and Health Policy and principles governing FENC production sites are as follows:
- The incorporation of new production lines, production processes or equipment is governed by Change Management Process. An application for change shall be filed and the process includes self-assessment on risk and control, change review/supervisor approval, pre-launch evaluation and closing.
- Risk identification shall be conducted to determine the risk level of operations associated with raw materials, products, activities and services which may potentially harm the operator, including workers (employees and contractors), or cause damages to equipment.
- Improvement goals shall be established based on risk levels and distribution of resources. Hardware improvement takes the priority, followed by control measures such as administrative management with special plans or operational guidelines. Implementation of the control measures are strictly monitored to minimize risks. Operation of control mechanisms is based on Regulations Governing Risk Identification, Assessment and Control set forth at each plant.
- Plans and implementations regarding overwork, workplace violence and the protection of the health of the middle-aged and elderly as well as maternity care at FENC production sites are conducted in accordance with local regulations. There were no irregularities in 2024.
- All production sites arrange risk control training for employees. In 2024, 127 sessions were held with 3,029 employees completing 7,354 training hours.
Hazard Recognition, Assessment and Analysis Procedures at Production Sites
.png)
Building Workplace Safety and Health with Labor-Management Participation
FENC establishes Occupational Safety and Health Committee at production sites, serving as the highest authority at each organization on the review and discussion of safety and health management. Setting up labor representatives in accordance with the seat ratio stipulated by regulations. The Committee convenes quarterly to determine the formulation, coordination and supervision of safety and health related issues at each plant to ensure full implementation. Contractors engagement and communication please refer to Stakeholder Dialogue and Sustainable Supply Chain Management.
Occupational safety and health management is one of the priority concerns when it comes to labor relations at FENC. The following subjects are included in the labor relations meetings, Occupational Safety and Health Committee meetings, and collective bargaining agreements with employees:
- Provide personal protective equipment.
- Implement labor relations management and establish the occupational safety and health committee with labor and employer representations.
- Involve labor representatives in the health and safety inspection, review and investigation.
- Provide job-related training for workers.
- A clear reporting and grievance mechanism for employees encountering health or safety issues is established to ensure their right to refuse unsafe work and protect them from being punished for the refusal.
- Schedule regular health checkups for workers.
- Comply with regulations from International Labor Organizations.
- Clearly establish safety and health goals and ways to achieve such goals.
The Occupational Safety and Health Committee
Operational Sites | Number of | Percentage of Worker |
Headquarters | 11 | 36% |
Hsinpu Chemical Fiber Plant | 29 | 34% |
Kuanyin Chemical Fiber Plant | 20 | 35% |
Kuanyin Dyeing and Finishing Plant | 37 | 46% |
Hukou Mill | 8 | 38% |
OPTC | 18 | 33% |
OGM | 19 | 53% |
FEFC | 13 | 38% |
FEIS | 32 | 75% |
WHFE | 20 | 40% |
OTIZ | 48 | 67% |
FEIW | 27 | 67% |
FEDZ | 63 | 60% |
FEAZ | 72 | 50% |
FEAV | 50 | 10% |
FENV | 27 | 15% |
FEPV | 158 | 59% |
FIGP | 45 | 67% |
APG Polytech | 10 | 50% |
| Note: All FENC production and operation sites are in compliance with the local regulations. |
Reinforcing Safety and Health Awareness Through Training
FENC provides regular training to make sure that every employee is familiar with occupational safety and health regulations as well as the management mechanism. The total occupational safety and health training hours accrued by FENC and contractor employees are 253,100 and 14,586 in 2024, respectively.
2024 Employee Safety and Health Personnel Training Statistics
Category | Number of Classes | Number of Trainees | Training Hours | |
On-The-Job Training on Safety and Health | 2021 | 993 | 19,967 | 84,031 |
| 2022 | 1,311 | 34,421 | 165,251 | |
| 2023 | 2,528 | 50,674 | 173,781 | |
| 2024 | 2,592 | 42,387 | 174,539 | |
Health Management Training | 2021 | 252 | 12,435 | 13,844 |
| 2022 | 272 | 11,961 | 15,046 | |
| 2023 | 376 | 13,341 | 14,914 | |
| 2024 | 486 | 16,042 | 19,437 | |
Hazardous Chemical Training | 2021 | 89 | 2,154 | 8,810 |
| 2022 | 140 | 3,295 | 19,925 | |
| 2023 | 176 | 4,431 | 18,669 | |
| 2024 | 191 | 4,277 | 22,041 | |
Protection Personnel Training | 2021 | 15 | 213 | 330 |
| 2022 | 20 | 213 | 412 | |
| 2023 | 26 | 281 | 569 | |
| 2024 | 20 | 139 | 243 | |
Emergency Response and Personal Protective Equipment Training | 2021 | 464 | 6,138 | 15,296 |
| 2022 | 337 | 10,860 | 20,052 | |
| 2023 | 615 | 14,654 | 33,229 | |
| 2024 | 652 | 14,113 | 27,434 | |
Internal Safety and Health Auditor Training | 2021 | 44 | 238 | 1,113 |
| 2022 | 31 | 444 | 3,252 | |
| 2023 | 129 | 2,858 | 7,046 | |
| 2024 | 59 | 778 | 3,762 | |
Risk Control Training | 2021 | 82 | 1,717 | 5,217 |
| 2022 | 54 | 2,046 | 3,782 | |
| 2023 | 55 | 2,705 | 6,387 | |
| 2024 | 72 | 2,140 | 5,644 | |
Total | 2021 | 1,939 | 42,862 | 128,641 |
| 2022 | 2,165 | 63,240 | 227,720 | |
| 2023 | 3,905 | 88,944 | 254,595 | |
| 2024 | 4,072 | 79,876 | 253,100 | |
2024 Contractor Safety and Health Personnel Training Statistics
Category | Number of Classes | Number of Trainees | Training Hours | |
On-The-Job Training on Safety and Health | 2022 | 725 | 7,201 | 36,996 |
| 2023 | 1,287 | 9,766 | 22,010 | |
| 2024 | 973 | 6,204 | 9,340 | |
Health Management Training | 2022 | 181 | 2,159 | 1,982 |
| 2023 | 625 | 2,827 | 2,570 | |
| 2024 | 283 | 1,921 | 1,149 | |
Hazardous Chemical Training | 2022 | 178 | 644 | 321 |
| 2023 | 529 | 1,444 | 1,187 | |
| 2024 | 193 | 1,426 | 654 | |
Protection Personnel Training | 2022 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2023 | 3 | 113 | 113 | |
| 2024 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Emergency Response and Personal Protective Equipment Training | 2022 | 222 | 874 | 1,067 |
| 2023 | 547 | 3,451 | 14,113 | |
| 2024 | 152 | 1,512 | 1,216 | |
Internal Safety and Health Auditor Training | 2022 | 1 | 24 | 24 |
| 2023 | 2 | 83 | 524 | |
| 2024 | 5 | 74 | 520 | |
Risk Control Training | 2022 | 41 | 505 | 899 |
| 2023 | 39 | 858 | 1,600 | |
| 2024 | 55 | 889 | 1,710 | |
Total | 2022 | 1,348 | 11,407 | 41,289 |
| 2023 | 3,032 | 18,542 | 42,117 | |
| 2024 | 1,661 | 12,026 | 14,589 | |
Chemical Safety Management
All production sites of FENC have established chemical management regulations of chemicals based on Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS).
Chemical management at all production sites places are according to the items as following:
- Chemical management at all production sites places an emphasis on source management. When procuring hazardous chemicals, the manufacturer, importer or supplier must provide the hazardous label and Safety Data Sheets (SDS). The same information is required when changes are made to existing data.
- When the chemicals arrive at the plant, on-site staff or the end-user must conduct examination based on the label, SDS and applicable regulations prior to acceptance.
- Post identification for hazardous chemical and prepare safety data sheet (SDS).
- The Company utilizes Chemical Control Branding (CCB) to evaluate the likelihood of exposure (usage and the degree of spread) and takes corresponding or control measures to mitigate risks. When changes occur to the types of chemicals as well as operational or production procedure, exposure assessment must be conducted again within 3 months before or after the changes occur.
- Waste liquids and containers for chemicals are disposed of and treated by qualified waste disposal companies in accordance with the regulatory requirements.
- To track and ensure the health of employees responsible for chemical operation, special health checkups are provided and their work environment is monitored every six months
Grievance / Reporting / Acceptance Mechanism Related to Hazardous Chemicals
.png)
Safety and Health Enhancement Campaign – Worker Engagement
1. The priority tasks implemented by the SHEF Task Force for FENC production sites in mainland China in 2024 are as follows:
- A total of 24 training sessions, amounting to 1,948 hours, were offered to address the needs of all units. A total of 770 people took part in the training, which covered a wide range of topics. The major focuses are safety risk identification and assessment; job safety analysis; chemical safety; safety observation; accident investigation; high-pressure pipeline safety; safety management for supervisors; fire emergency response and rescue.
- FENC production sites in mainland China recorded 12 cases of occupational injuries in 2024, capping the number within the target that had been set for the year, which is no more than 13 cases. The number represents a 25% drop from 2023. In addition, FENC was able to keep the total recordable injury frequency below 0.2 for the first time, showing progress in the overall safety performance, which shall continue.
- The SHEF Task Force assisted FEDZ and FEIW in the implementation of jurisdictional management in 2024, and on January 1, 2025, the task force started providing such assistance to FEAZ. Currently, jurisdictional management has been implemented at all FENC production sites in mainland China.
- Incident reporting has been implemented and encouraged, including the reporting of near-misses and minor injuries, to develop a culture with proper workplace incident management. The task force facilitated the sharing of past occupational injury incidents from FENC production sites as a precautionary reminder to prevent future occurrences.
- The SHEF Task Force collected and shared 56 newly enacted government regulations concerning safety and health.
- Outreach and assistance for establishing intelligent systems: FEAZ established an incident reporting system and online training system; FEDZ created an equipment and facility accounting system; FEIW built an incident reporting system.
- The SHEF Task Force led the peer exchange campaign among FENC production sites in mainland China. Specific activities include sending senior electrical specialists to identify hidden dangers at each plant; helping FEIW with the construction safety audit targeting the airbag project to maintain steady progress.
- Four issues of the SHEF quarterly magazine were published in 2024. The content, which was gathered from all FENC production sites in mainland China, featured special coverage on electrical safety, special equipment, emergency response and occupational health. The magazine also shared articles with valuable insights from external sources.
2. Performance Review for the Occupational Safety and Health Management System at FEFC
To encourage business entities to implement self-management over occupational safety and health, the Ministry of Labor has commissioned accredited agencies and local labor inspection offices to conduct review over occupational safety and health management systems. FEFC took the initiative and proposed a performance review over its safety and health management system, which has been approved by the Ministry of Labor with a validity period between June 29, 2024 and June 28, 2027.
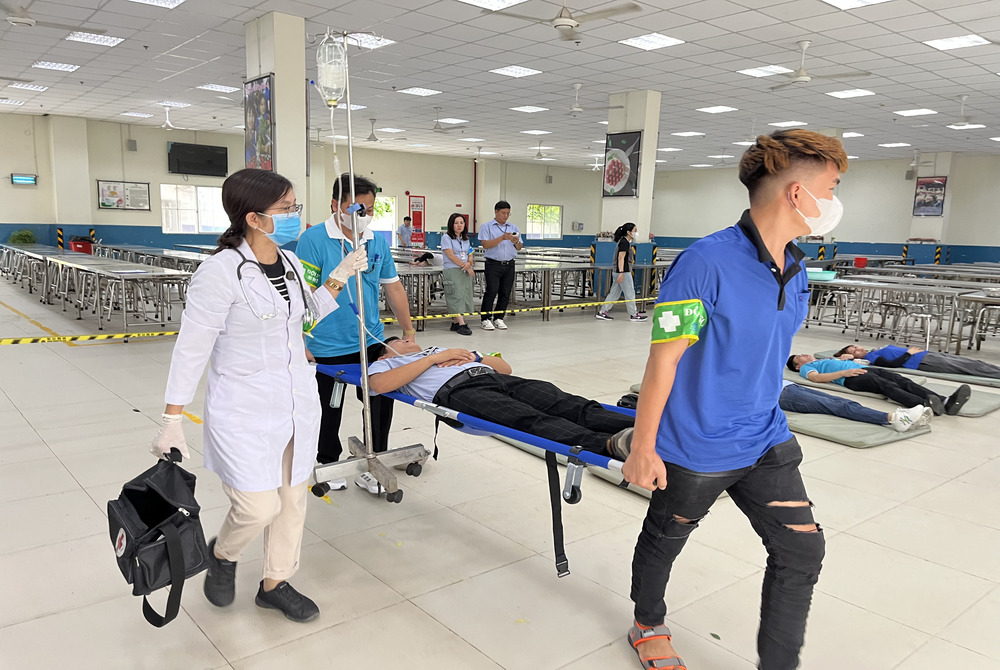
Strengthening Emergency Response with Safety Drills
To activate emergency response at the earliest possible moment and minimize injuries, fatalities and production losses, FENC conducts hazard identification and risk assessment for its production sites by factoring in geographical environment, hazardous chemicals used, distribution of natural disasters and disasters that are fire-inducing. The results then dictate the control measures as well as emergency response procedures, training and drills targeting various disaster scenarios and probabilities to be established for each production site.
During an emergency, all production sites shall follow the protocol established for emergency response and notification procedure. Staff shall identify the disaster, notify applicable units and personnel, and engage in damage control to keep the situation from worsening. Ongoing assessment shall be made to the on-site conditions to minimize harm to the staff, property and environment with adequate treatment to prevent secondary disasters. The investigative unit shall conduct thorough reviews over the cause and propose improvement strategies. A report shall be presented and the unit responsible for the emergency shall undergo educational training to prevent future occurrence.